Humble Beginnings
There’s growing excitement around Decentralized Finance, better known as DeFi, and for good reason: DeFi is bringing sweeping changes to finance, investing, and the way money moves.
But where did DeFi come from, and what do its origins say about where it’s about to take us?
DeFi seems so complex to newcomers that it can feel hard to understand. But there’s a way to get your head around it, and that starts with travelling back in time.
Let’s take a step back…before Bitcoin, PayPal, credit cards, and drive-through ATMs to get some perspective. Then you’ll see why DeFi is being called Finance 3.0 — and how Finance 1.0 and 2.0 became endangered species.
Want to know more about Decentralized Finance? Everything you need to know is in our book! Available NOW on Amazon!
Finance 1.0: Starting with Central Banks
The last few centuries — and especially the last few decades — have seen many innovations in financial products and services. But despite consistent progress, there weren’t a lot of big breakthroughs in the way money is managed and organized — for everyday people, businesses, or institutions.
Today, the economies of most of the world’s nations are tied to their central banks decisions and policies, a system that was effectively invented centuries ago and helped usher in Finance 1.0 a.k.a “Traditional Finance.” In the United States the central bank is the Federal Reserve (or just “The Fed”), in China it’s the People’s Bank of China, and in Sweden it’s the Sveriges Riksbank — originally founded in 1668.
The original employees of the Sveriges Riksbank would be amazed to visit the 21st Century today and see how much hasn’t changed with Finance 1.0. In fact, they would instantly recognize their traditional mix of a centralized banking system that manages the circulation of the national fiat currency — government-issued money that isn’t backed by something like gold.
Finance 1.0 kept things moving, but it has plenty of problems. With roots in the 1600’s, it’s a system built on a long-obsolete set of organizing principles — rules now seriously out of sync with the hyperconnected, extremely interdependent economics of the 21st Century. Finance 1.0 is a slow-moving method of defining, allocating, and using money/credit/value/wealth that’s no longer a fit for today’s light-speed economics.
Over time, Finance 1.0’s shortcomings became easier to see, especially for people and businesses who want to work efficiently together in our global economy. Slow transactions, high fees, the possibility of human error, and complex cross-border transactions, are just a few of legacy finance’s hazards. Not to mention the very real danger of theft, as well as sudden changes in government sanctions and regulations.
Finance 2.0: Fintech Comes Next
Finance 1.0 laid the foundation. Fintech — finance + tech — finally followed to form Finance 2.0.
Fintech leverages the 20th Century’s huge technological leaps, converged to enable money’s next major shift. Computers became exponentially smaller and more powerful, Internet connectivity flourished, cellular networks gained bandwidth, and mobile devices got more affordable and sophisticated.
All these gains drove Fintech, developing the next generation of apps and services for mobile banking, investing, and lending. Have you ever paid a friend with Venmo, or seen an ad for Rocket Mortgage’s online application?
That’s Fintech/Finance 2.0 in action, and it led to the mass adoption of centralized user-friendly stock trading platforms like Robinhood and eToro, or Revolut’s all-encompassing personal financial planning app. Finance 2.0 modernized Finance 1.0 by digitizing banking systems, and connecting buyers and sellers of all kinds to payment providers like Stripe.
These are tools we’re all familiar with, that we hear about every day. Finance 2.0 brought on a lot of big advances — so what’s the problem?
It’s true that Fintech allows millions of Millennials and Gen Z investors to easily access the stock market. But Fintech also has many structural flaws, and as those have come to light they’ve led to movements like WallStreetBets (WSB), a forum on Reddit where people discuss stock and options trading — often with the goal of questioning Wall Street rules as they pursue profits.
Robinhood selling information about its users’ stock market activities to the financial services giant Citadel Securities may have allowed hedge funds to front-run (trade ahead of a significant price change) retailers, a sure sign that Finance 2.0’s goals of democratizing access to financial markets is flawed.
This came after WSB members banded together to organize a short squeeze (a sharp stock price increase that forces traders who bet the stock price would fall to quickly buy the stock to prevent even more losses) in Citadel’s short position (a bet that a stock price will go down) in GameStop. It was a fast-paced sequence of events that caused several hedge funds to lose $19 billion in total.
To cap it off, Robinhood and other brokerages limited the trading of GameStop and other similarly shorted stocks for several days. It was an essential maneuver to keep themselves in business, as well as satisfy regulators, even if it meant infuriating their users and appearing to run counter to their stated purpose of providing equal access to the stock market.
The chaos showed that Finance 2.0 is not as well organized, predictable, and “bug-free” as everyone thought it was. Social media was able to disrupt, at least temporarily, wealthy Wall Street institutions and create huge losses for some blindsided institutional investors. While a forum on Reddit isn’t going to single handedly take down Citadel Securities, with $35 billion assets under management (AUM), the GME drama shows change is coming.
Yesterday’s finance cannot power tomorrow’s prosperity. Bailouts, taxes, nationalization, and regulations dominate the news. These measures can temporarily limit the negative economic impact of disasters like the COVID pandemic. But what they’re not doing is building a more efficient, productive, and effective financial system.
Let’s reimagine finance for the 21st century. Here’s why — and how.
Finance 3.0: The Revolution
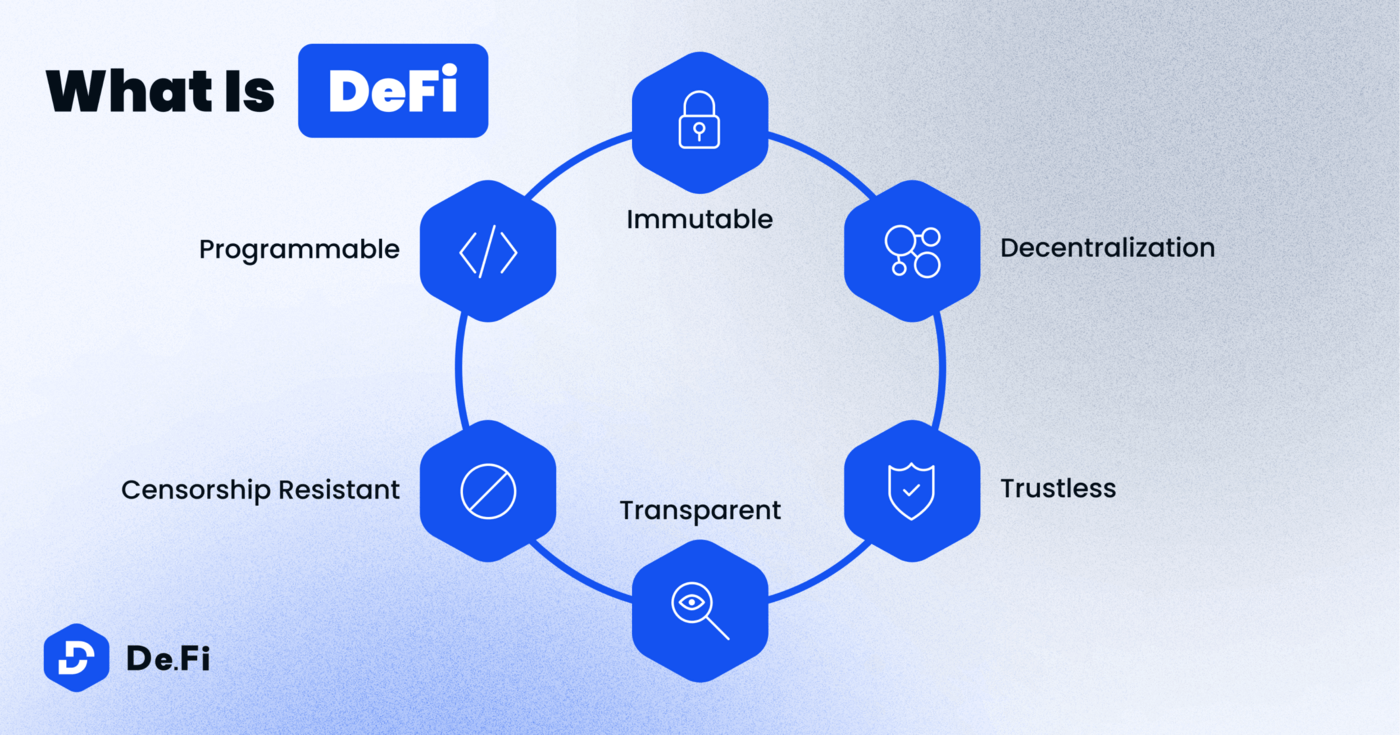
This is where things finally start to open up: Finance 3.0 is the open financial system, where the decentralized finance of DeFi becomes a reality. It goes beyond Fintech to provide more controls that empower its users. DeFi takes out the middleman, while eliminating fees, charges, and penalties.
Finance 3.0 is what’s called a “permissionless” system.
It’s independent of borders and communities, and doesn’t require anyone’s approval for participation. That’s a very different idea for finance, which has earned its reputation for putting up barriers to taking part, especially as the rewards get bigger.
The ideal engine to power Finance 3.0 is blockchain technology, a time-stamped series of data records that is decentralized — managed by a global network of computers without a single owner, the records on a blockchain are almost impossible to change. The most famous example of blockchain in action is Bitcoin, which has benefited from blockchain’s unprecedented approach to scalability, transparency, and security.
The vision of a more fair and transparent Web dates back to around 2006, but the tools and technologies weren’t available then for it to materialize. Bitcoin was still three years off, bringing with it the notion of blockchain’s distributed ledger for peer-to-peer digital storage. Decentralization was the idea; blockchain was the means. It led to human-centered finance — Finance 3.0.
So what happens when finance becomes human-centered? Some key highlights:
No central point of control: Middlemen are removed from the equation. Blockchains like Ethereum provide a trustless platform (i.e. one whose encryption and protocols mean that trust is not required between participants — they can trust in the code). The rules are unbreakable and data is fully encrypted.
Central banks do not control transactions in Finance 3.0. No government or regulator will have the ability to freeze accounts and assets, as long as they can’t steal the private keys to your crypto wallet.
For example, in the DeFi cryptocurrency exchange Uniswap, anyone who wants to can list any ERC20 token (a type of Ethereum-based cryptocurrency) for sale. You can do this in a trustless manner that leaves you free to buy, trade, and swap it with other users — no bank, broker, or brokerage app needed. To many people, the decentralized flow of DeFi feels very liberating!
Non-custodial: Finance 3.0 puts the user in complete control of their digital assets, if that’s what they want. Instead of having to keep your cash or funds custodied in a bank account, you have a non-custodial option where you retain the ownership of your digital assets in your own non-custodial wallet, with no third party involved. No one else can freeze or access your funds. For those who seek security against a bank or government seizing your accounts, non-custodial matters.
Ownership of data: From central banks to tech giants like Amazon and Facebook, huge data centers are storing information on your income, credit cards, interests, dietary preferences, and much more. If you think it’s just so they can improve their services, think again: marketers and advertisers pay billions each year for the data.
In Finance 3.0, end users are regaining complete control of their data, thanks to the security of encryption. Information can be shared on a case-by-case, permissioned basis via cryptography techniques like the zero knowledge proof%20is,the%20truth%20of%20verified%20property.) (ZPK), which allows one party to prove to another party that they know a particular fact, without revealing any other information besides that fact. ZPKs keep the information that must be shared between two parties to a minimum.
Uninterrupted service: Account suspension and network attacks like distributed denial of service are dramatically reduced. That’s because there’s no single point of failure in a decentralized system, so service disruption to accounts or networks will be minimal. In Finance 3.0, entire datasets are stored on distributed nodes to ensure redundancy, while multiple backups prevent server failure or seizure.
Permissionless blockchains: Anyone can create an address and interact with the network. The power to access permissionless chains just can’t be overstated: Users cannot be barred on account of geography, income, gender, orientation, or other sociological and demographic factors. Wealth and other digital assets can be transferred cross-border, quickly and efficiently, worldwide.
If you wanna stay safe and be up to date — subscribe to our newsletter! We will send you our DeFi Security Handbook straightaway. You can expect insights, interesting content and updates from us.
How Does DeFi Work?
Like any emerging technology, Finance 3.0 and its child DeFi are still being refined. For access to DeFi, people will only need a seed phrase — a single password asset which enables their interaction with decentralized apps (dApps) and other services. Individuals will still use a Web browser to access the Internet, and visually these DeFi tools will be as user-friendly as the best of Finance 2.0.
Your personal transition from 2.0 to 3.0 should feel like a gentle learning curve. But behind the scenes, the framework connecting you with digital services is complex: Transactions are signed and verified manually, to prevent platforms from siphoning away personal information without due cause. Web users opt in to DeFi platforms rather than trying — and often failing — to opt out.
So, what are some things that are different in Finance 3.0?
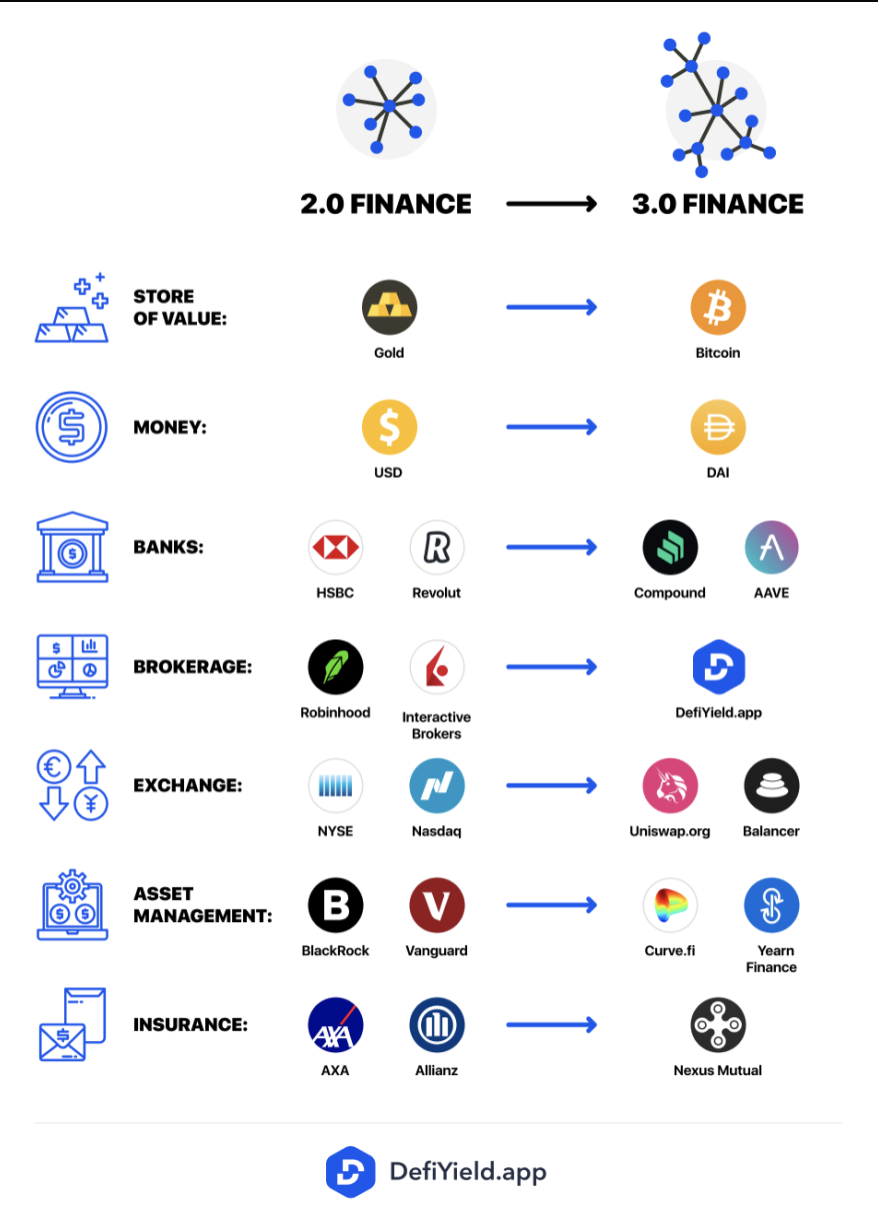
- Instead of Gold or fiat currency, we have assets for trustless transactions like Bitcoin or the Dai stablecoin (a stablecoin is a cryptocurrency whose value is tied, or pegged, to an oustide asset like the US dollar).
- Instead of the traditional centralized bank like HSBC, or digital banking like Revolut, non-custodial solutions lending protocols like Compound or Aave allow you to get loans or borrow assets in a completely trustless manner.
- Instead of brokerage accounts like Robinhood and Interactive Brokers, you can use easy-to-use DeFi dashboards like De.Fi as your gateway to Finance 3.0
- In addition to centralized crypto exchanges like Coinbase and Binance, Crypto trading happens on fully decentralized exchanges (DEX) like Uniswap and Balancer — anyone who uses these DEXs can create or add liquidity to customizable liquidity pools and earn trading fees.
- Insurance is transformed, from the Finance 2.0 online quotes for car insurance from Axa or Allianz. Next is the 3.0 model of Nexus Mutual which allows people to leverage and share risk without needing an insurance company — instead, smart contracts have you covered.
3.0 Here We Go!
The examples above are just the beginning. As Finance 3.0 roars into action, new DeFi platforms will emerge with a healthy level of competition, and they can’t be held back by the legacy financial providers.
But the best is definitely yet to come: The most popular dApps and decentralized services that we’ll be using three years from now have almost certainly not been invented yet.
The near-future DeFi timeline looks something like this:
At present the decentralized apps, wallets, platforms, and other digital assets that make up Web 3.0 — Internet networks powered by decentralized protocols — are scattered. Accessing these interfaces calls for separate seed phrases, logins, and identities — much like the existing Web 2.0.
Soon, innovations like the De.Fi ecosystem will link everything together via a single seed. Because this will operate as an encrypted key that can be associated with its owner, De.Fi will provide proof of identity — without giving up any more of your identity than necessary.
Just as Fintech didn’t totally replace traditional finance, the move to DeFi requires time and integration with existing online systems. The wheels are already turning, and the train is leaving the station. Hop on board, and you can benefit from DeFi and its fascinating new direction. Finance 3.0 is a revolution in motion.
The change can happen faster with your help: Please share this article! Fire away in the comments with questions, criticisms, or your own ideas for revolutionizing finance.
Check our guides:
Solana Network Ultimate Yield Farming Guide [Infographics]
Fantom Network Ultimate Yield Farming Guide [Infographics]
Huobi ECO Chain Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
Polygon Network Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
Binance Chain Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
And join us on Twitter and Telegram!
Good luck in farming!