A Database of DeFi Scams, Hacks and Exploits
Table of Contents
Why we built the Rekt Database
How to access the Rekt Database
How to use the Rekt Database
Getting Started
Reviewing events in detail
Using filters to review events by type
Rug pull
Flash loan attack
Abandoned
Exploit
Bank Run
How to access the Rekt Database via API
Today, we are announcing the launch of our Rekt Database — the first fully-featured database of DeFi scams, hacks and exploits — which is another groundbreaking service within our superpowered DeFi portfolio tracker.
As you know, the main aim of De.Fi is to create a safe place to access DeFi, to protect users from any potential risks that occur as a result of smart contract vulnerabilities or malicious project owners who want to scam them. This is why we released the Open Audits Database as part of De.Fi ecosystem earlier this month and why we are announcing the launch of the Rekt Database today.
Our crypto hack database is a key weapon within the De.Fi safety armoury that helps users combat these threats. It has been built manually and painstakingly by our team over a number of months. What the team has created is a valuable store of all key information concerning rug pulls, which will help to prevent other malicious actors from attempting the same scams in future. Educate yourself and avoid losing your gains from crypto bull runs!
The Rekt Database contains the following key information:
•A database of more than 2 500 scams, hack and exploit events
•The total of all funds lost across all these events (yes, we calculate this number)
•A full breakdown of all technical issues that occurred
As you can see, this will become an important resource for all DeFi users and everyone who is interested in building this industry into a safe and accessible community where anyone can thrive. Worried you’re NGMI? Investigate the Rekt Database!
Why we built the Rekt Database
Looking back to the first few months of the DeFi Summer in 2020, the market was full of questionable projects, which had been forked from high-quality protocols with well-judged economic models.
These developments had been driven by the exponential growth of DeFi early on, as users tried to make life-changing amounts of money overnight and scammers looked to take advantage of this desire.
As a result, a whole range of ‘fast food’ scam projects appeared. These were backed by malicious developers who employed a range of tactics to appear trustworthy while attracting TVL and dazzling their unsuspecting victims with promises of significant DeFi yield farming returns.
It was against this backdrop that our team started the hard work of helping DeFi users to remain safe by avoiding these scams. Our work involved auditing projects based on the community requests and releasing the Open Audits Database to help users understand which projects could be trusted.
The launch of the Rekt Database, a fully-featured database of scams, hacks and exploits, is the latest milestone on our never-ending journey to keep DeFi safe.
How to access the Rekt Database
You can use this link to access our crypto hack Rekt Database.
If you are using Metamask, Coinbase Wallet, WalletConnect, Authereum or Torus you will be able to access it through these DeFi wallets to get additional features in the future.
Stay tuned to our community and social channels to find out more!
How to use the Rekt Database
Getting Started
The first thing you’ll see when you use the Rekt Database is the Total Funds Lost across all known scams, hacks and exploits.
Why? Well, it can be a painful number to see but we think it’s really important that all DeFi users see what a big problem this is, so we can all work towards ending this issue.
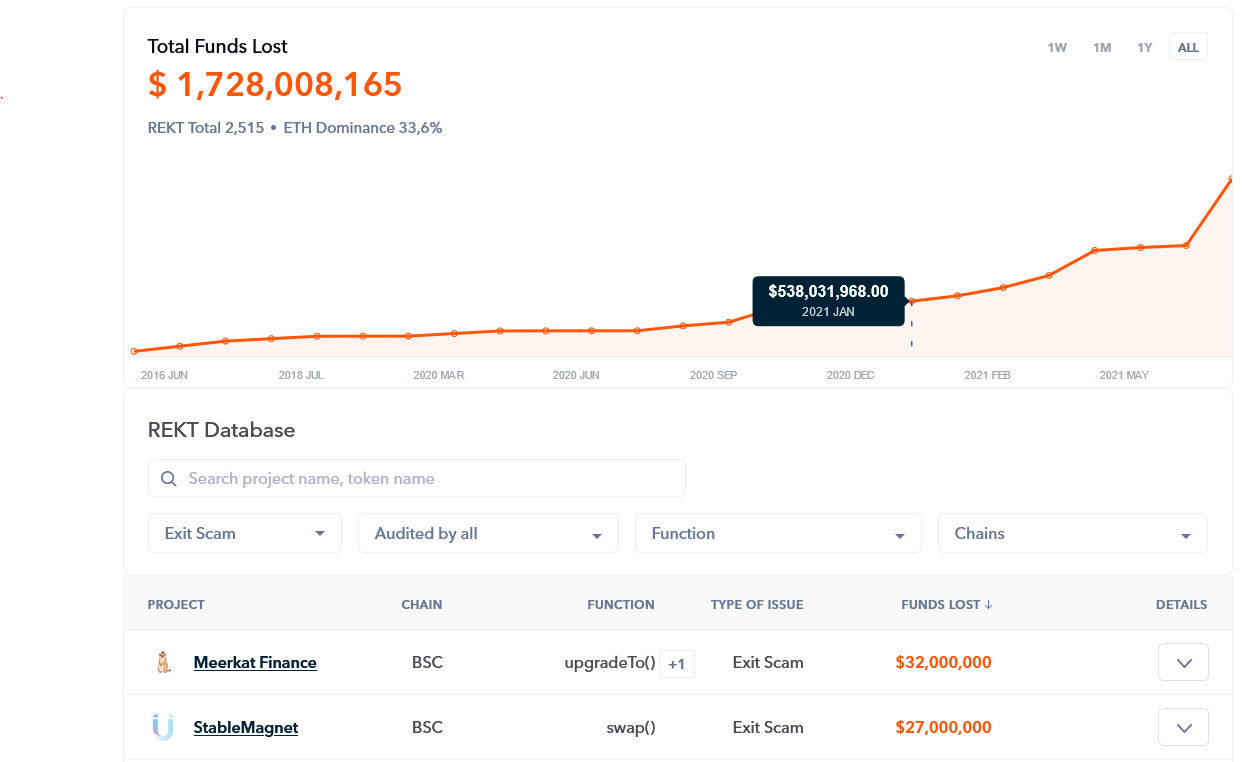
Also, on the right hand side, you can see the button to report a claim if you have been affected by malicious projects or vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
The process is simple. Once you have reported a claim, our engineer will verify the report. If the claim is substantiated, our engineer will review the case by analyzing on-chain activity and, if the event is valid, it will be added to the database.
Reviewing events in detail
The most useful feature of the Rekt Database for the majority of users is the database of scams, hacks, honeypots, and exploits, and the breakdown of each event as shown in the image below. The database contains more than 2,500 events, starting from Summer 2016.
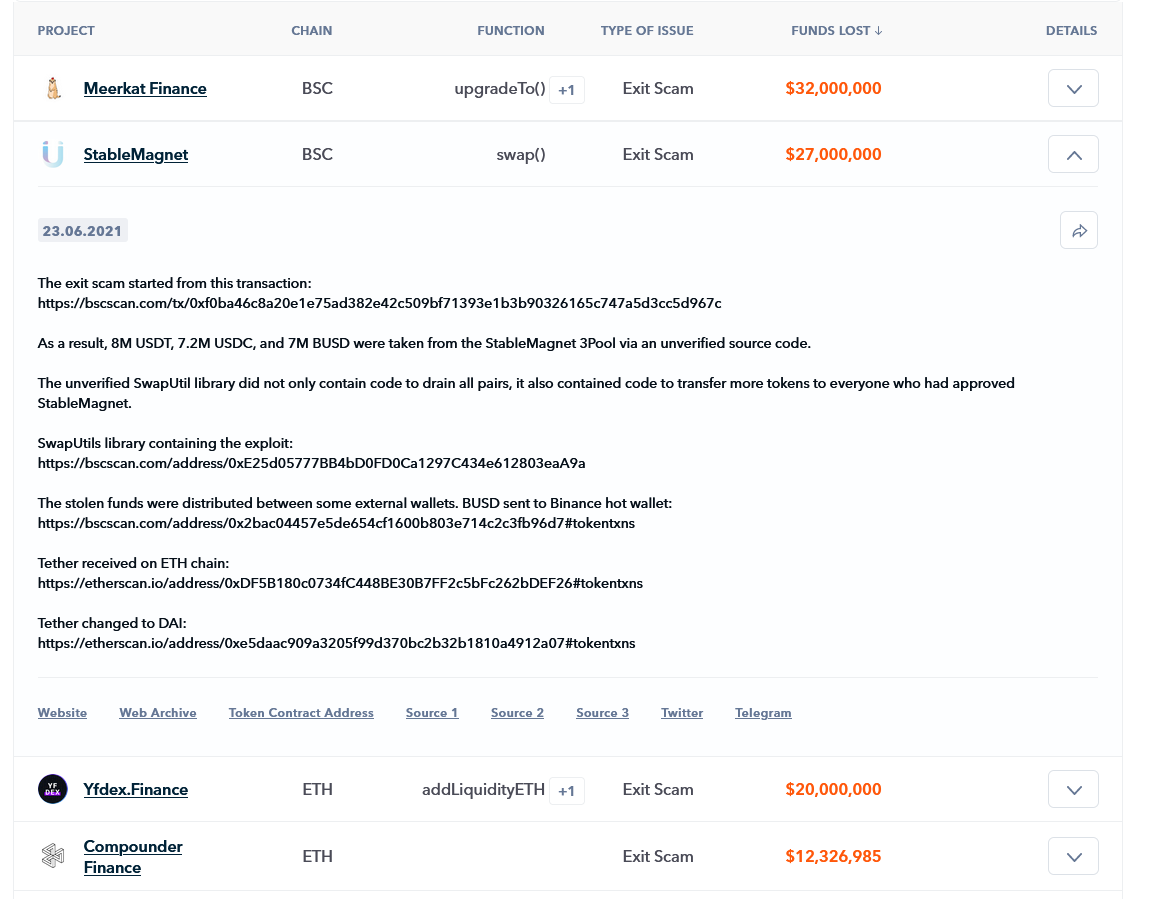
Every event entry includes the following details in its breakdown:
Project name
•Token ticker
•Accessible address on the appropriate chain
•Date of the rug pull, based on an analysis of on-chain activity
•Tech issue, verified by one of our Solidity engineers
•Malicious function
•Funds lost, based on movements between fraudsters’ addresses
•Detailed description of the event
•Links to proofs, project media
Most event entries include web archived sources that you can use to verify any related information. You can also use the search functionality to find interesting cases within the database that relate to specific keywords.
Using filters to review events by type
You can also use the “Type” filter at the top of the screen to review events by the type of issue involved. These event types have been categorized as follows:
Exit Scam
Exit Scam involves harmful actions planned by the development team, who aimed to steal depositors’ and investors’ funds. Mostly this category contains real facts of the malicious actions from the project team side, based on the on-chain analysis.
Flash Loan Attack
Flash Loan Attack involves an attack with the external vector made by a hacker on the target protocol. It results in tokens’ price imbalances with the further loss of lenders’ funds.
Abandoned Project
The term “abandoned project” means social media inactivity, stopping development progress, that has slowed the project’s growth, caused it to be neglected, or culminated in complete responsibility abandonment from the project team side.
Smart Contract Exploit
Smart Contract Exploit involves an external or, in some circumstances, an internal attack vector that employs a smart contract with malicious logic. The reason for this is revealed flaws and weaknesses in a project’s smart contract code which are used in order to hijack a project and drain users’ funds.
Bank Run
For now, bank run relates only to the Iron Finance case, when users have panicked after the huge token sales and started withdrawing funds so therefore algorithmic mechanisms stopped working properly and it caused even more withdrawals and total depletion funds in the liquidity pools and vaults.
How to access the Rekt Database via API
As with other De.Fi Safety services such as the Open Audits Database, our revoke permissions tool, and smart contract scanner, The Rekt Database API is open for everyone to use.
Companies, projects and individuals can request API access to the Rekt Database and an authorization token will be used to perform requests from De.Fi. At the moment, users who request this are given access to Audit Lists and Audits By Token Addresses, which you can learn more about on our **Github page.**
Our API strategy aligns perfectly with the overriding mission of De.Fi to keep users safe and secure within DeFi, by providing them with high-quality tools and working to improve security across the decentralized finance industry.
If you want to access the Rekt Database straightaway, you can do so here: https://de.fi/rekt-database.
Check our guides:
Best Upcoming Crypto Airdrops for 2023
The Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming with Binance Chain
Will Crypto Recover? – 2023 Market Outlook
And join us on Twitter and Telegram!
If you want to stay safe and be up to date — subscribe to our newsletter! We will send you our DeFi Security Handbook straightaway. In the ebook we explain how to stay safe, what are we paying attention to when performing a smart cotract audit, and what should you do to not get REKT. You can expect insights, interesting content and updates from us.