Interoperability, scalability and security are three of the most important issues in blockchain. They are also the three big promises at the heart of Polkadot’s vision for the future of the web.
This multi-chain protocol, which has been built by one of Ethereum’s most important co-founders, is now getting the attention it deserves from retail and institutions alike. To many, it provides a glimpse of the future of blockchain and the mass adoption of this technology.
For all these reasons, this is the perfect time to investigate the staking and yield farming opportunities that exist on Polkadot. In this guide you’ll find all you need to get started and learn all the important information about the project, its architecture, bridges, wallets and other key technical features.
What is Polkadot?
Polkadot is a blockchain network that supports a range of different connected blockchains, which it refers to as parachains, in order to provide a scalable, interoperable and secure ecosystem for the next web. It describes itself as an ‘open-source protocol built for everyone’.
Polkadot’s base layer provides shared security for the network, with each parachain having its own application-specific design, which include components that allow each parachain to meet its particular needs. This is possible because everything built within the Polkadot ecosystem uses a modular framework.
“Polkadot is one of the most exciting emerging blockchain ecosystems in the industry, with a number of DeFi projects on the rise.” — Messari Crypto Research
Some of the key features and benefits of Polkadot include:
- True interoperability
- Economic and transactional scalability
- Easy blockchain innovation
- Forkless and future-proofed
- Security for everyone
- User-driven network governance
Polkadot is a multi-chain application environment that allows data to be transferred across blockchains, whether those be public, open and permissionless blockchains or private and permissioned ones. It has been built to connect blockchains so they can exchange information and transactions in a trustless way via the Polkadot relay chain.
Polkadot’s goal is to enable a completely decentralized web where users are in control. The Polkadot vision of the future web is one where users’ identities and data are their own, safely secured from any central authority.
“Some teams have really lost sight of the fact that decentralization and security are not optional features here. This is not something that we can cut corners on.” — Dr. Gavin Wood, Co-Founder of Polkadot.
Dr Gavin Wood, who is also one of Ethereum’s co-founders, started to work on the idea for Polkadot as a ‘sharded version of Ethereum’ in 2016.
The first version of the Polkadot whitepaper was released in October 2016 and the Web3 Foundation, a Swiss non-profit that supports Polkadot research and development as well as overseeing funding, was established in 2017. The first token sale also occurred in 2017 and this laid the groundwork for the development and rollout of Polkadot’s mainnet, which occurred in stages throughout 2020.
According to Messari, Polkadot has the most venture capital and hedge fund participation of any blockchain project, with Three Arrows Capital, Pantera Capital and PolyChain Capital some of its most well-known backers.
Polkadot’s Architecture
The key technology at the heart of the Polkadot network is Substrate, a blockchain-building framework developed by Parity Technologies.
The Polkadot state machine is compiled to WebAssembly, a standard that was developed by major companies including Google, Apple and Microsoft. The runtime environment is coded in Rust, C++ and Golang, which are all common programming languages.
The Polkadot network has a number of key features that help it to achieve its aim of providing a scalable, interoperable and secure ecosystem for the next web. These include the Kusama network, which acts as a canary network for Polkadot, as well as the elements described below.
The Relay Chain
This is the chain at the heart of Polkadot that is responsible for shared security, consensus and cross-chain interoperability, which all parachains interact with.
Parachains
These are sovereign blockchains with application-specific designs and individual components optimized to their particular use case.
Parathreads
These are similar to parachains but differ in the respect that they provide a pay-as-you-go security model for blockchains that don’t need constant network connectivity.
Bridges
Bridges allow parachains and parathreads to connect with one another, as well as communicate with external blockchain networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Consensus
Polkadot uses a hybrid consensus mechanism that aims to improve on Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake systems, which both make a network vulnerable to attack until the point where the community is sufficiently large to support it.
The Polkadot approach allows blockchains to pool their security from day one, so that security is aggregated and applied to everyone.
Consensus mechanisms
Consensus is powered by two mechanisms working in tandem:
BABE
The Blind Assignment for Blockchain Extension (BABE) is the block production mechanism.
GRANDPA
The GHOST-based Recursive ANcestor Deriving Prefix Agreement (GRANDPA) is the finality gadget for the Polkadot relay chain.
Consensus participants
There are a number of network participants who collaborate to reach consensus:
Nominators
These secure the relay chain by selecting trustworthy validators and staking DOT tokens.
Validators
These secure the relay chain by staking DOTs, validating proofs from collators and interacting with other validators.
Collators
These maintain shards by collating transactions and producing proofs for validators.
Fishermen
These monitor the network and report bad behavior to validators.
Governance
In July 2020, governance was transferred to the network’s on-chain system, which involves a range of different entities, as described below.
Token holders
DOT tokens are used to participate in governance decisions, such as tabling proposals, voting and bonding.
Council members
Members are elected to represent passive stakeholders for proposing referenda and vetoing dangerous or malicious referenda.
Technical Committee
This consists of teams that are actively building Polkadot. With the council, the committee can propose emergency referenda and fast track implementation.
$DOT Token
The DOT token is Polkadot’s native token. It can be used for governance over the network, staking and bonding, as well as for paying fees.
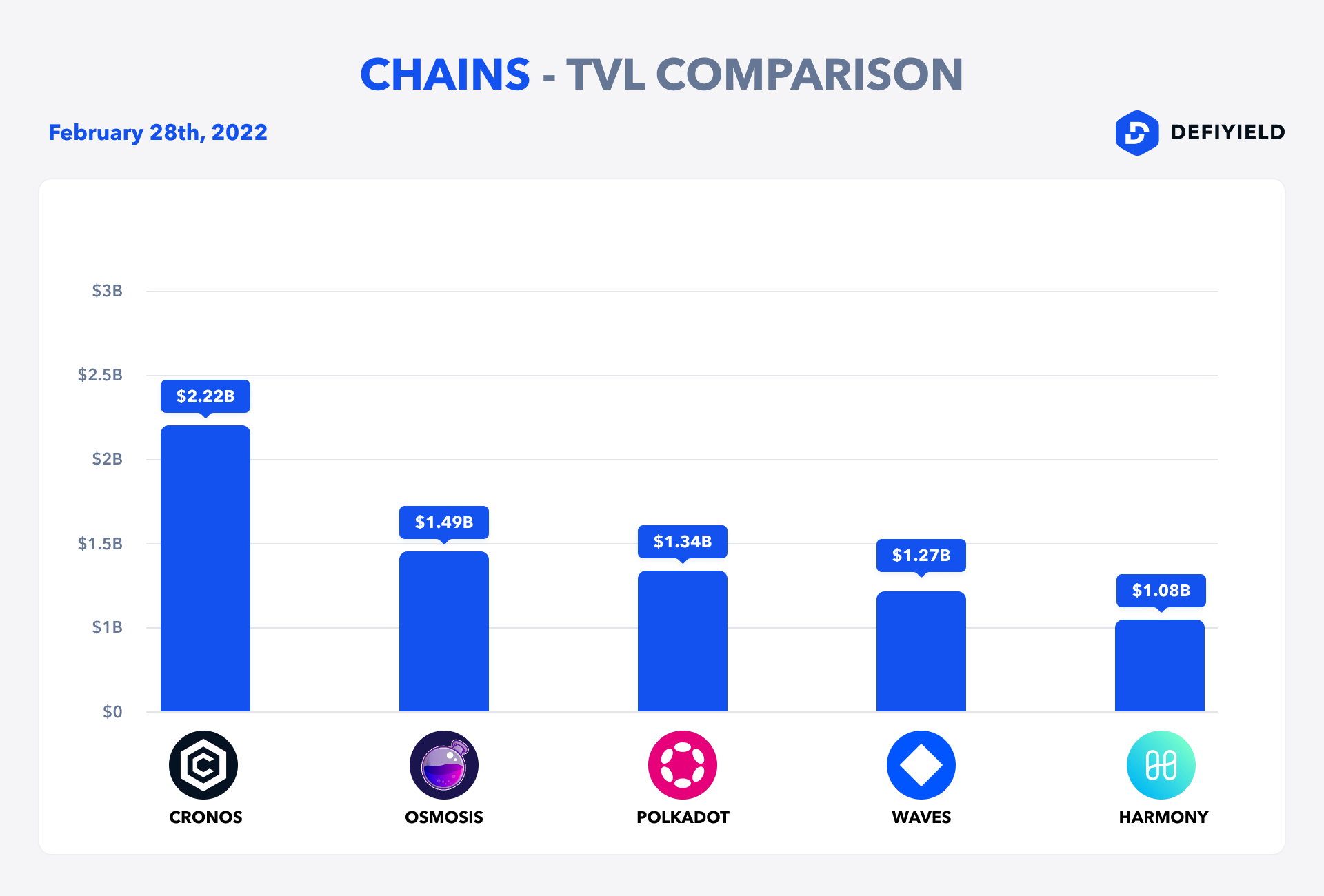
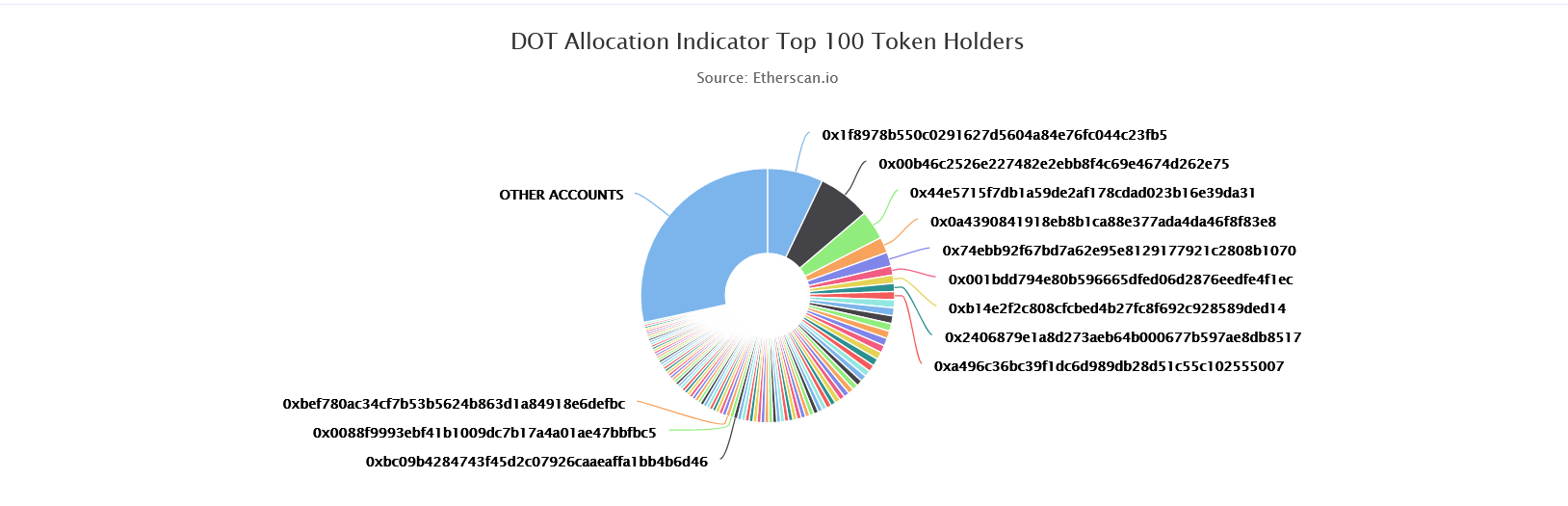
As of 28 February 2021, DOT has a total supply of 1,169,661,110, a price of $16.93 and a current market cap of $18,416,003,748 (according to CoinGecko data).
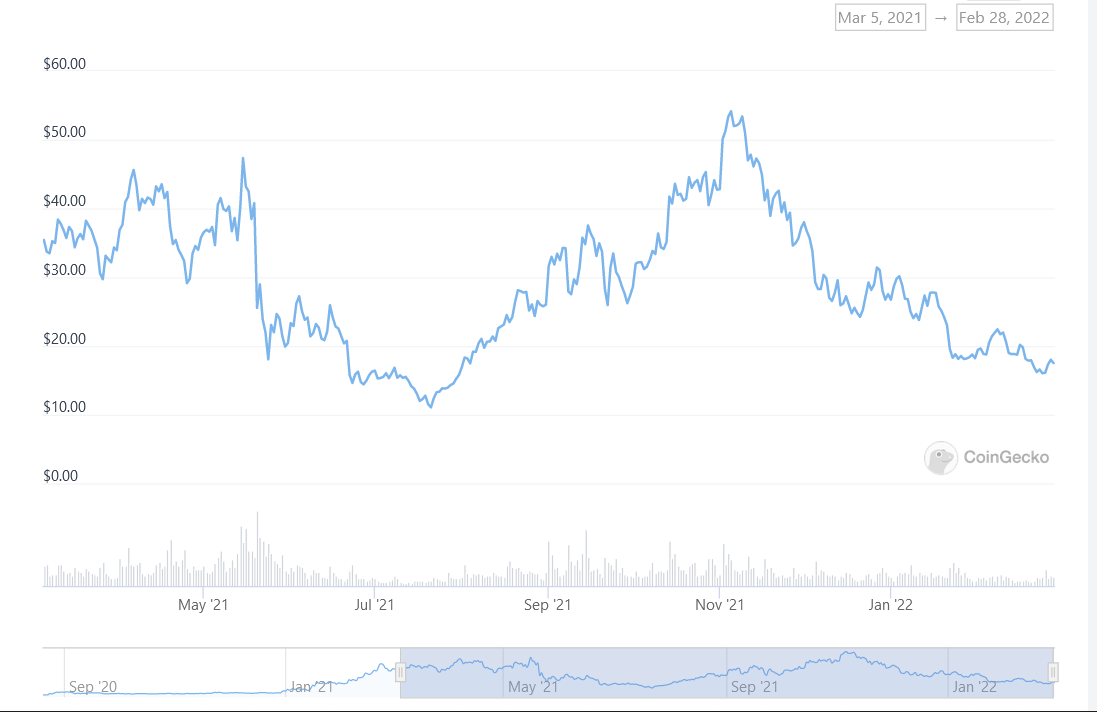
The Polkadot Ecosystem
The Web3 Foundation is working with a range of entities to build Polkadot and develop the services and applications that run on it. This includes providing grants for development in order to build the Polkadot ecosystem.
Examples of existing projects include smart contract chains, data curation networks, oracle chains, identity chains, financial chains, Internet-of-Things chains, Zero Knowledge privacy chains, file storage chains and much more.

Wallets for Polkadot
There are various wallets available for Polkadot, including popular multi-chain options, as well as specific Substrate wallets developed by the team at Parity Technologies.
Polkadot JS
Polkadot JS is a browser-based vault for managing all aspects of your Polkadot account and DOT holdings. It is developed and supported by Parity Technologies.
Parity Signer
Another wallet tool developed by the Parity team, Parity Signer allows you to turn an old smartphone into a hardware wallet for Polkadot and other Substrate-based chains.
MathWallet
MathWallet is a multi-platform crypto wallet with mobile, desktop, hardware and extension functionality, which can be used to store Polkadot tokens.
Ledger
Ledger is one of the most established hardware wallets available today. It supports sending and receiving DOT tokens but cannot be used to participate in crowdloans.
Bridges for Polkadot
Bridges are integral to Polkadot achieving its goal of being an open-source protocol built for everyone, which allows data to be transferred across blockchains.
Bridges to and from Polkadot are enabled either by bridge contracts, which are smart contracts that connect Polkadot’s relay chain to an external chain, or bridging modules, which are purpose-built to help external chains connect with Polkadot.
Some examples of Polkadot bridges that are being developed at present are listed below.
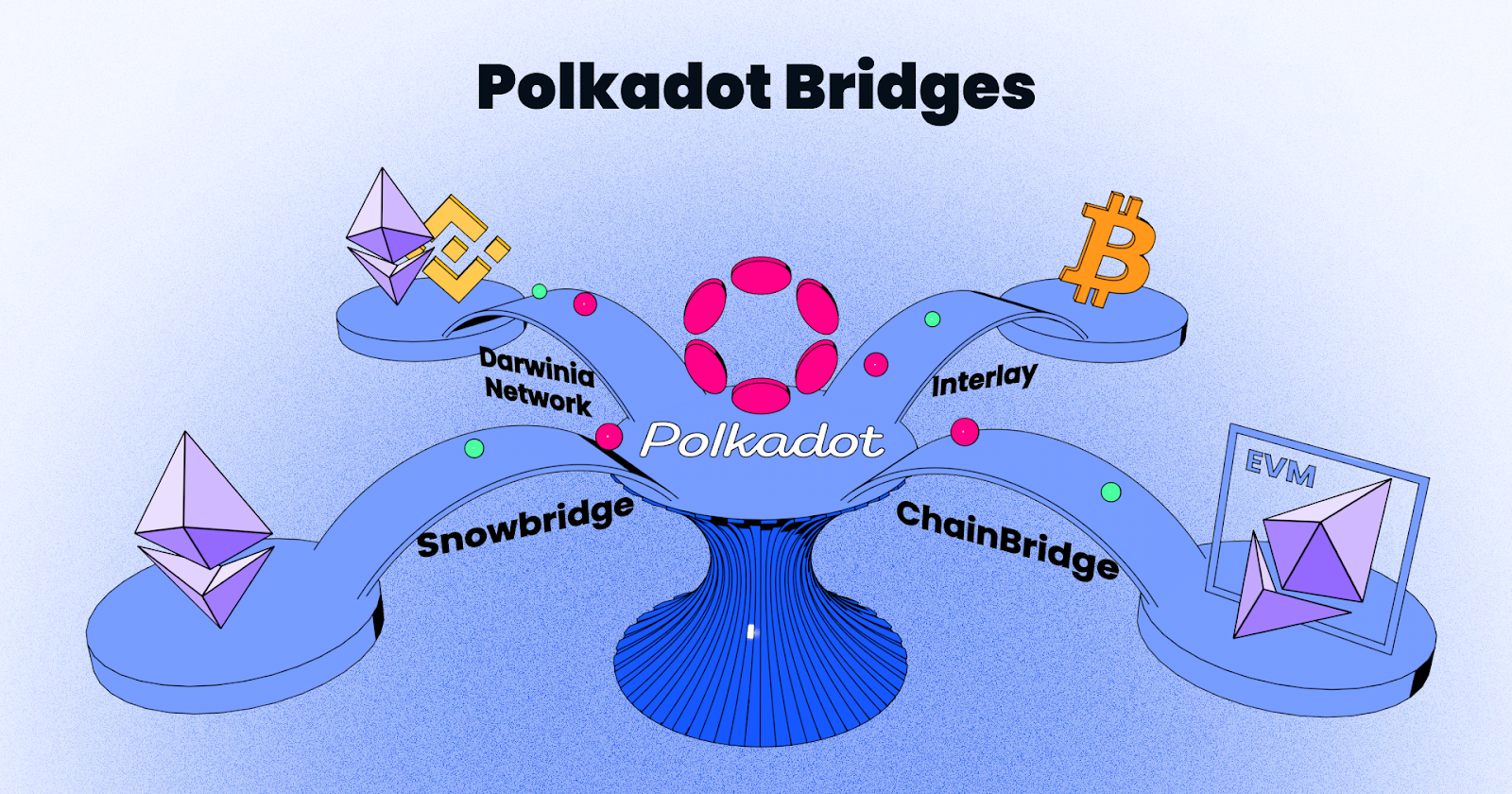
Interlay
Interlay is building a trustless bridge between Bitcoin and Polkadot called interBTC, which is currently a testnet.
Snowbridge
Snowbridge is a general purpose, trustless and decentralized bridge between Polkadot and Ethereum that is being built by Snowfork.
Darwinia Network
Darwinia is a Web 3.0 cross-chain bridge hub that provides an entrance into Polkadot for public blockchains like Ethereum and BNB Chain.
ChainBridge
ChainBridge is an extensible cross-chain protocol built by ChainSafe that supports bridging between EVM and Substrate-based chains.
Yield Farming on Polkadot
As mentioned above, Polkadot is a blockchain that supports parachains built-on it and therefore completes mainly the infrastructure role.
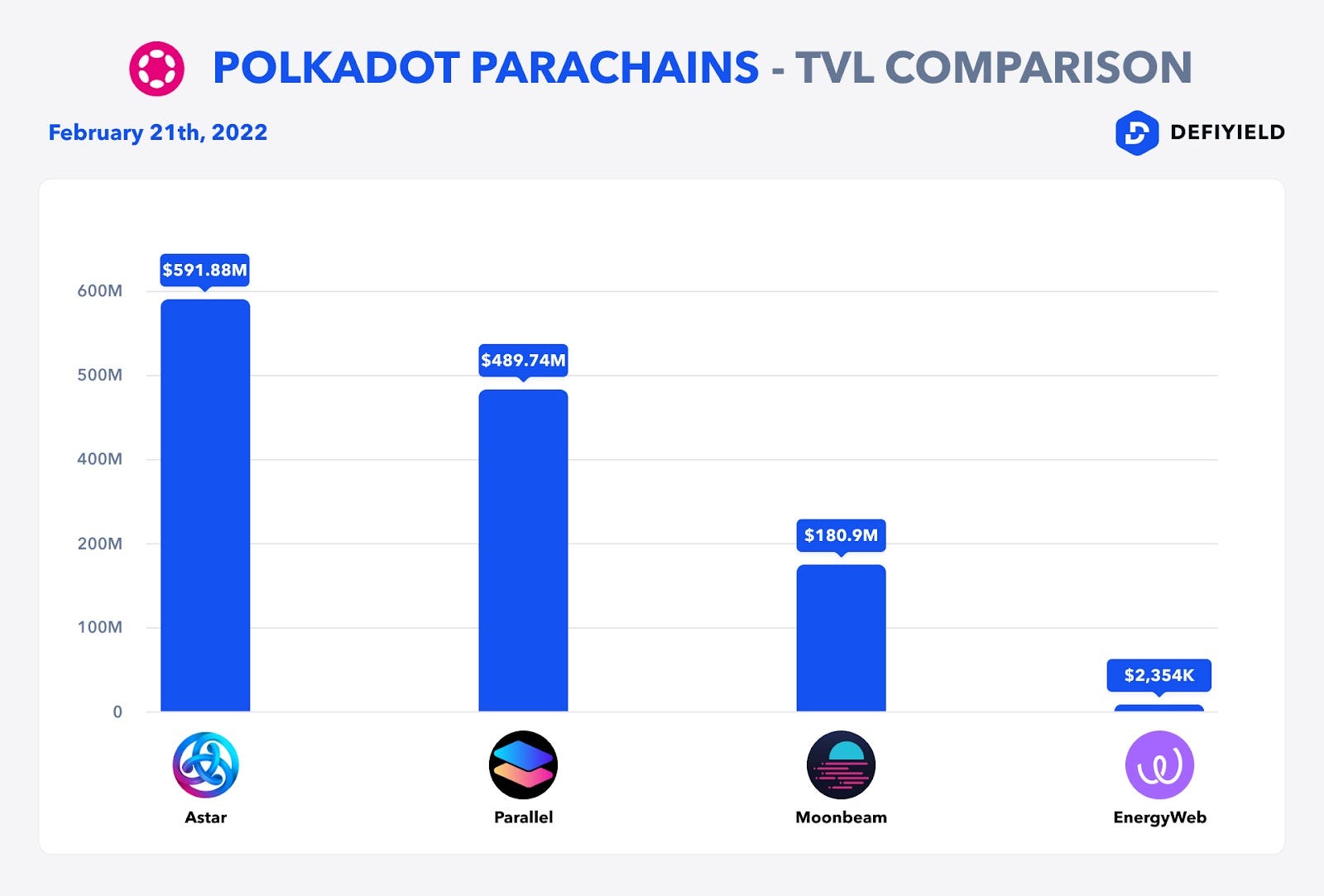
There’re a lot of different yield farming opportunities on the networks that are built on Polkadot, such as Moonbeam, Acala, Astar Networks.
For each of these chains you can find a bunch of staking and yield farming opportunities and we are planning to release guides about them.
Should I use Polkadot for Staking and Yield Farming
Polkadot is a developing ecosystem that hasn’t reached full maturity yet but is still gaining a huge amount of attention, as the recent auctioning of slots for the first parachains has shown.
At a time when the Ethereum community is talking more and more about the main chain providing a shared security layer for layer two, dapp and sidechain solutions, Polkadot has been building for this future from day one.
Polkadot is not just about the future though, as there are DeFi, staking and yield farming opportunities that already exist or are set to go live very soon. For all these reasons, investors with an eye on what the next big thing might be should definitely consider Polkadot’s ecosystem and the chains that are built on it.
However, as always, this is not investment advice and you should always do your own research first.
Here you can check yield farming opportunities on other chains: de.fi/explore
Check our guides:
Tezos Ultimate Yield Farming Guide [Infographics]
Solana Network Ultimate Yield Farming Guide [Infographics]
Fantom Network Ultimate Yield Farming Guide [Infographics]
Huobi ECO Chain Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
Polygon Network Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
Binance Chain Ultimate Guide for Yield Farming
EOS Ultimate Yield Farming Guide
Arbitrum Ultimate Guide [Infographics]
The Ultimate Yield Farming Guide For Terra Blockchain (Luna) [Infographics]
The Ultimate Guide to Avalanche Network
Ultimate Guide to Yield Farming on Harmony (with infographics)
Ultimate Guide to Tron Network [Infographics]
The Ultimate Yield Farming Guide For Moonriver Network
The Ultimate Yield Farming Guide For Celo
The Ultimate Yield Farming Guide For KuCoin Community Chain
The Ultimate Yield Farming Guide For NEAR Protocol
And join us on twitter and telegram!
Good luck in farming!